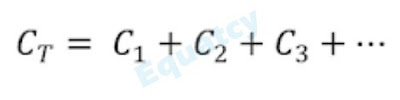|
1) Electric potential of a charged object
Q = C V
WHERE :
Q = charge
C = Capacity
V = Potential difference
NOTE: This equation is used in case of capacitor problems.
©Equatcy
2) Capacitance
WHERE :
C = Capacitance
A = Area
ε = Permittivity of Media
ε(0) = Permittivity of in Air
d = Distance between the plates
k = Relative Permittivity
NOTE: This equation is used to measure the capacity of a capacitor practically. When a “ k ” (Permittivity) solution is used instead of air, the capacity of the capacitor increases.
©Equatcy
3) Field intensity of a Capacitor
WHERE :
E = Field intensity of a Capacitor
A = Area
ε = Permittivity of Media
ε(0) = Permittivity of in Air
Q = Charge in area
k = Relative Permittivity
NOTE: The field intensity of a capacitor is a vector, and the formula is derived by Gauss's theorem and the electric flux equation.
©Equatcy
4) Series capacitor systems
WHERE :
1 / C (total) = Total Capacitance
NOTE: In a series capacitor system, the potential differences across each capacitor are different.
©Equatcy
5) Parallel capacitor systems
WHERE :
C (total) = Total Capacitance
NOTE: In a Parallel capacitor system, the potential differences across each capacitor are same.
©Equatcy
6) Electrical energy of a capacitor
WHERE :
E = Electrical energy of a capacitor
V = Potential difference
Q = Charge
C = Capacitance
NOTE: The other two equations are derived using the Q = C V equation.
©Equatcy