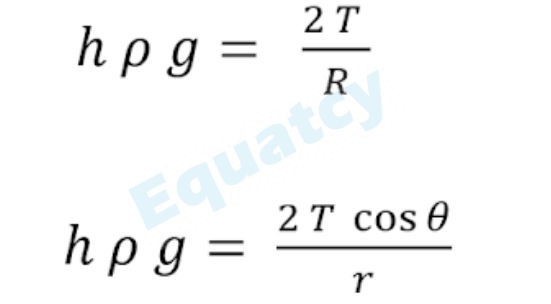1) Surface tension force
F = T l
WHERE :
F = Surface tension force
T = Surface tension coefficient
l = Length of the imaginary line
NOTE: This equation can be used to find the surface tension force exerted by the liquid surface on a liquid surface and any contact object.
©Equatcy
2) Pressure difference in a liquid bubble
WHERE :
P(1) = Pressure inside the liquid bubble
P(2) = Pressure outside the liquid bubble
T = Surface tension coefficient
R = The radius of the liquid bubble
NOTE: This formula can be used to find the pressure gap on either side of a spherical liquid path.
©Equatcy
3) Pressure difference in an air bubble
WHERE :
P(1) = Pressure inside the air bubble
P(2) = Pressure outside the air bubble
T = Surface tension coefficient
R = The radius of the air bubble
NOTE: This formula can be used to find the pressure gap on either side of an air bubble. The pressure gap doubles because there is air on either side of the liquid film.
©Equatcy
4) Surface tension Energy of liquid surface
WHERE :
E = Surface tension Energy of liquid surface
T = Surface tension coefficient
∆ A = Area difference
NOTE: Whenever the surface area of a liquid surface changes, the surface energy is stored or released.
©Equatcy
5) Capillary uptake of a liquid
WHERE :
cosθ = Radius of the pipe is the ratio of the radius of the path
T = Surface tension coefficient
ρ = Density of liquid
h = Height of the liquid stem
g = Gravitational acceleration
R = Radius of the path
r = Radius of the tube
NOTE : In case of a capillary deviation, the value is (-).
©Equatcy
6) Surface tension force of a liquid film
F = 2 T l
WHERE :
F = Surface tension Force of a liquid film
T = Surface tension coefficient
l = Length of the imaginary line
NOTE: Since there is air on either side of the liquid film, the force doubles.
©Equatcy